Par Value Vs Market Value Shares

Market value is the current price at which the common shares of a company change hands meaning the market s point in time estimate of the company s value less the debt.
Par value vs market value shares. This has no relevance to the value of either in the market. Par value vs face value. Meaning it s a point in time consensus estimate of the millions of people financial institutions insider traders of what the company is worth. In other words it is the amount that the share holder wi.
Face value and par value are investment terms that are related to bonds and stocks. The value or par value recorded by the corporation varies from the selling price or market value of the stock or bond. Par value is the nominal or face value of a bond or stock or coupon as indicated on a bond or stock certificate. Par value of shares also known as the stated value per share is the minimal shares value as decided by the company which is issuing such shares to the public and the companies then will not sell such type of shares to the public below the decided value.
For delaware corporations the par value is typically set at 0 0001. Book value is the net worth of the company per share. Also called nominal or face value the par value is the minimum price per share that must be paid in order for the shares to be considered fully paid. Individual investors buy and sell corporate bonds and shares of stock on a daily basis.
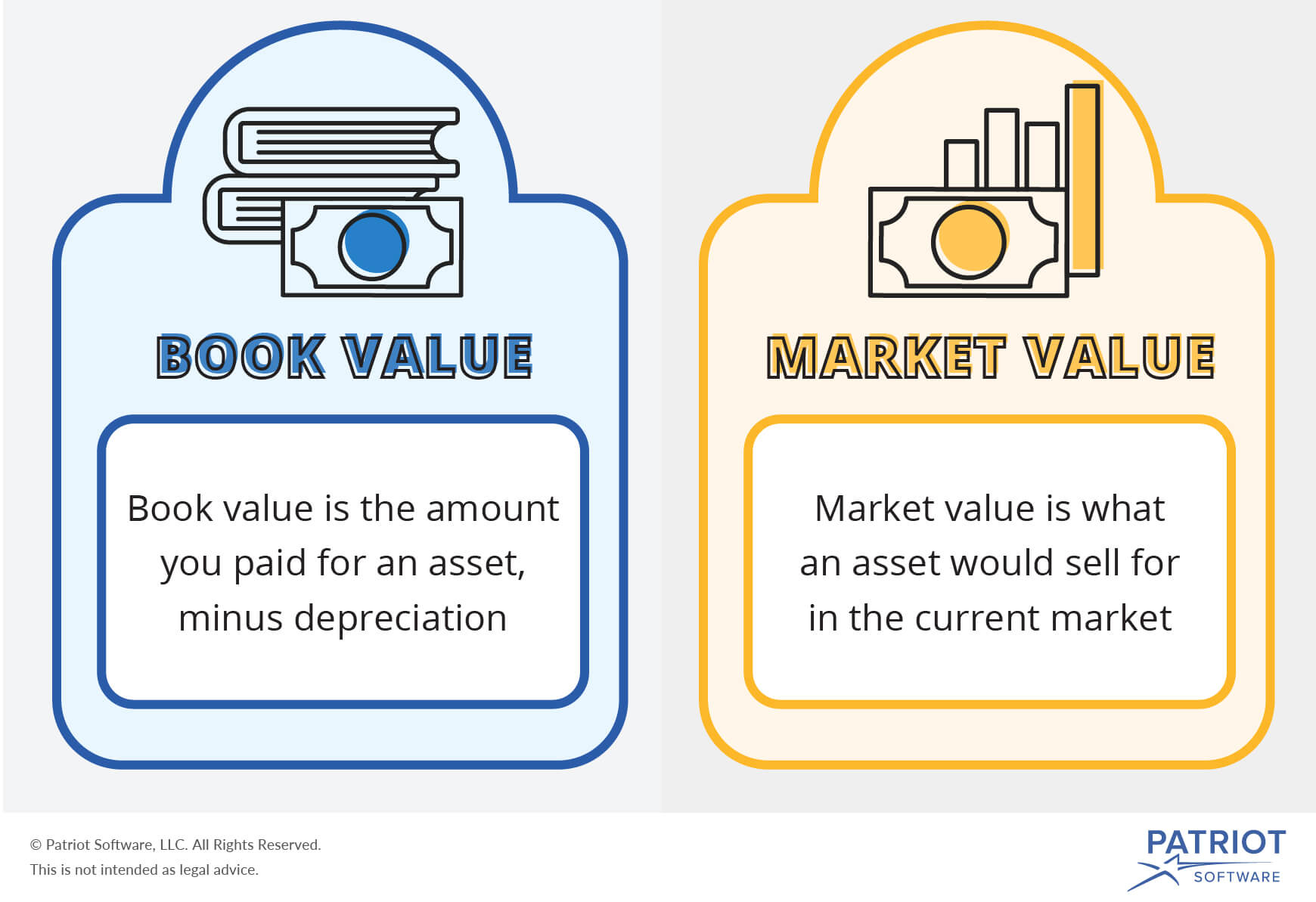
A par value stock unlike a no par value stock has a minimum value per share set by the company that issues it. What is par value of share. Initial offerings are made available at par value of the face value to make them look attractive after listing and the stocks mostly open at a rate higher than the face value bringing profits for the investor. Par value is the issue price of a security or stock book value is the value derived from the balance sheet of a stock where the value of stock is given by the sum of equity and reserves divided by number of shares in issue while market value is the on going price of a security determined by market forces of demand and supply.
It is a static value determined at the time of issuance and unlike market value it doesn t fluctuate on a regular basis. Stock and bond prices fluctuate based on company earnings economic factors and dividend declarations. The par value has no bearing on the fair market value of the stock.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/thinkstockphotos_493208894-5bfc2b9746e0fb0051bde2b8.jpg)



/GettyImages-1058454392-146fd62a8b20476fa0888ecfa18868ae.jpg)



